P12-3: Interaction of the airway epithelial barrier and T helper (Th) 2 cells during helminth infection of the lung
Sandra FreierPhD Student
Sascha KahlfussProject Leader |
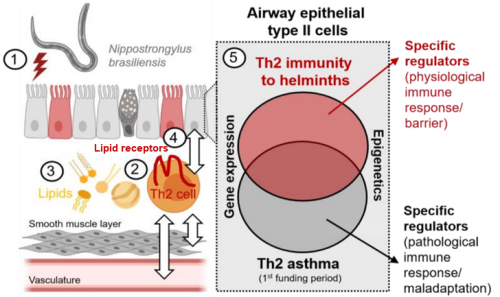
T helper (Th) 2 cells play a detrimental role in allergic airway inflammation, but also mediate immunity against helminths such as Nippostrongylus (N.) brasiliensis. N. brasiliensis is a gastrointestinal nematode that infects the host at larval stage 3 (L3). Further maturation occurs within the lungs, which results in the onset of respiratory symptoms. During this phase of lung infection, the initial immune system responders emerge. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) and dendritic cells (DCs) migrate in, and ILC2s release type 2 cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, IL-9 and IL-13. Following parasite infection, the adaptive immune response is directed towards a T helper (Th) 2 cell response, which is instrumental in recruiting basophils and leads to an isotype class switch to IgE.Th2 cells are therefore one of the key players in the immune response and clearance of parasite infection. In contrast to this protective Th2 immune response, Th2 cells also mediate overshooting immune responses during allergic asthma. In addition, recent studies and our own preliminary data suggest a strong dependence of Th2 cells on lipid metabolism pathways during Th2 asthmatic airway inflammation (Project 12-2). However, yet it is incompletely understood how the interaction between Th2 and airway epithelial cells differs during physiological (immunity to helminths) and pathological (allergic asthma) immune responses. In project 12-3, we will therefore investigate how the lipid receptors regulate Th2 cells and their interaction with the airway epithelium following N. brasiliensis lung infection, with the ultimate goal of comparing the role of lipid metabolism in Th2 cells and their interaction with the airway epithelium during immunity to helminths and allergic asthma. To this end, we will use genetically engineered mice and apply bulk transcriptomics and single cell RNA sequencing. Our project could have significant implications for precision and personalised medicine, for example in the development of novel therapeutics that target pathogenic Th2 cells in allergy without compromising immunity to infection.
Th2 cell-dependent effects on the airway epithelial barrier during chronic asthma and lung helminth infection. 1) Components of N. brasiliensis activate alveolar epithelial type II cells. 2) Primed T cells differentiate into Th2 cells and migrate to the lung. Here, Th2 cells secrete the Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. 3) Metabolites such as lipids (ox. LDL, free fatty acids) activate lipid receptors in lung Th2 cells. 4) Lipid receptors in Th2 cells is important for the interaction between Th2 cells and the airway epithelia in immunity to helminths (hypothesis). 5) Comparison of gene expression and epigenetic regulation in alveolar type II cells during chronic asthma and lung helminth infection. Abbreviations: Th2 cell, T helper 2 cell. |
Photos: by UMMD, Melitta Schubert/Sarah Kossmann