Key goals of RTG 2408
Chronic diseases constitute a major health threat and pose an increasing burden on health systems. Central mechanistic aspects in chronic diseases are cellular maladaptation and misdirected cellular communication at physiological barriers. Highly specialized cells, such as endothelial or epithelial cells, define physiological barriers. Dysregulation and -function of these cellular barriers may result in a disease-promoting micromilieu. The latter is characterized by a specific secretome and the activation and maladaptation of local and inflammatory cells. Moreover, important to disease chronification is the perpetuation of the maladaptive process. Mechanistically, perpetuated disease processes depend on altered cellular signalling, resulting in molecular fixation of the disease process. Currently, our understanding of the molecular changes underlying maladaptation at physiological barriers and leading to chronic diseases is limited.
Within our RTG we aim to characterize disease-defining maladaptive processes at endothelial and epithelial barriers. In systematic approaches, we analyze gene expression, molecular signalling and molecular networks (e.g. NF-κB system) in endothelial and epithelial cells and their impact on barrier function.
The comparative studies of these two barrier-defining cell-types provide the opportunity to exchange ideas and to combine experimental tools (e.g. animal models, organoids, co-culture systems) and technical approaches (e.g. high resolution 3D-imaging, intravital 2-photon-microscopy, mass spectrometry), thus, generating an added value for the young researchers. Additionally, the involvement of medical students and clinicians generates an environment fostering translational research. Thus, we train young scientists in a highly relevant research area and by exposing them to timely methodology and state-of-the-art approaches our RTG prepares the young scientists for their independent research careers.
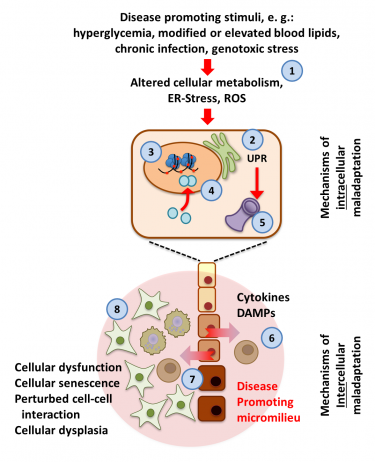 |
Maladaptive response at physiological barriers in chronic diseases. Pathologic stimuli (1) impair adaptive cellular processes (e.g. unfolded protein response, UPR, 2). These changes promote protein modifications and regulation of histones (3), transcription factors (4) and other regulators of key cellular functions (e.g. proteostasis, 5), perpetuating the maladaptive response. The resulting dysfunction of endothelial or epithelial cells at physiological barriers generates a disease promoting micromilieu (6), characterized by cellular dysfunction of barrier-defining cells (yellow to brown; dark colouring reflecting an altered cellular phenotype, 7) and recruited inflammatory (green, 8) cells. These changes may dispose to cellular dysplasia. |
Click here for details of all individual projects
Individual Projects of Cohort 3
Individual Projects of Cohort 2
Individual Projects of Cohort 1