P8-1: DNA binding protein A is a key regulator of mitochondrial function that promotes renal ischemia/reperfusion injury
Charlotte ReichardtPhD Student
Peter MertensProject Leader |
Our previous data demonstrate that following acute kidney injury cold shock proteins Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) and DNA binding protein-A (DbpA) control cell recruitment to activated tubular cells and direct tubular cell phenotypes and survival. The function of YB-1 is highly context-specific, as mice with heterozygote YB-1 knockdown show diverse responses to injuries: following ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) the tubular damage is enhanced, whereas following tubular obstruction (UUO) damage is markedly reduced. Furthermore, we recently showed that high salt diet (HSD)-induced proximal tubular phenotypic activation and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 expression are coordinated by YB-1. In addition, we identified Notch-3 as receptor for extracellular YB-1. In the absence of receptor Notch-3 tubular cells are unresponsive to cell stress and lack canonical NF-κB activation. Renal tubular epithelial cells are amongst the most metabolic active cells in humans with susceptibility to injuries (e.g. toxins, hypoxia) and orchestrate immune cell recruitment. If perpetuated, these processes lead to maladaptive responses, cell death and breakdown of the barrier functions in isolated nephrons. Tissue architecture devoid of tubular barrier function results in vascular rarefication and organ fibrosis. Collectively, cold shock proteins determine tubular cell fate decisions in an injury-specific manner. Elucidation of the underlying mechanism(s) during acute kidney injury is the focus of this project.
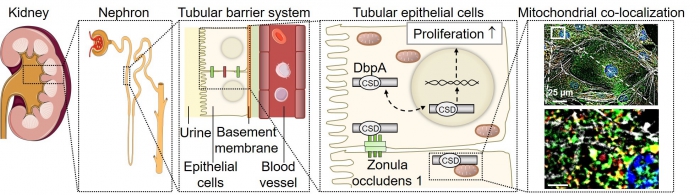
Tubular barrier system. The nephron is the smallest functional unit of the kidney and consists of a glomerular corpuscle and the tubular system. The tubular barrier is formed by epithelial cells and basement membranes and is supplied by adjunct blood vessels. In tubular epithelial cells DbpA is located at the cell membrane and upon tubular cell dedifferentiation may shuttle from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and coordinate proliferation. Furthermore, DbpA was detected as mitochondrial protein as it co-localizes with mitochondrial marker proteins. |
Photos: by UMMD, Melitta Schubert/Sarah Kossmann